RTD temperature sensor accuracy
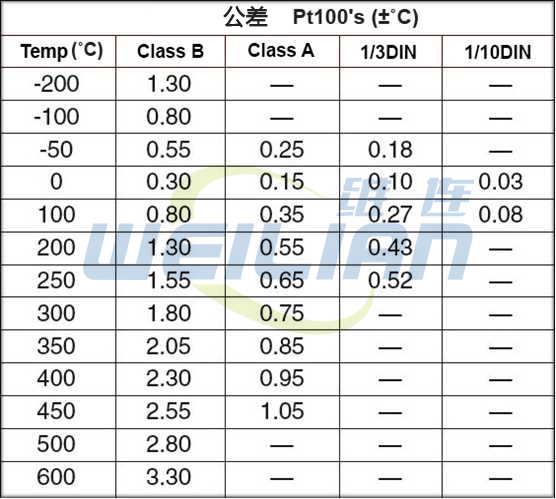
RTD temperature sensor accuracy IEC 60751:2008 is considered as an international standard and specifies the tolerances for platinum RTD elements. The two most common tolerances for Pt100 RTD temperature sensors are Class A and Class B. For closer tolerances, 1/3 DIN and 1/10 DIN standards are available. The higher the element tolerance is, the wider the range of deviation from the temperature resistance curve is, which increases the level of uncertainty. Although strictly speaking, this does not make the 1/10 DIN detector more accurate than the Class B detector, it does significantly reduce the uncertainty of reading. The following table shows the tolerances for Class A and Class B detectors defined in DIN 43760, and then use these standards to find out the tolerances for 1/3 DIN and 1/10 DIN detectors. As you can see, the tolerance of Class B detector is ten times higher than that of 1/10 DIN detector, which means that the reading uncertainty of Class B detector is ten times higher than that of 1/10 DIN detector. It should be noted that the tolerances defined in the following table are only applicable to bare sensors and do not take into account the design or construction of a complete sensor.
Uncertainties
When trying to define the accuracy of RTD temperature sensors, three main uncertainties need to be considered:
• Detector tolerance
• Uncertainty caused by sensor structure
• Uncertainty of calibration procedure
The second and third points are difficult to predict accurately because self heating and stem conduction must be considered.
Self heating effect
When electric energy is applied to the resistor, it will generate thermal energy, which in turn will radiate heat, thus generating uncertainty, which is called self heating effect.
At high temperature, it has little influence on temperature and temperature measurement, but at low temperature or when accurate measurement is required, the heat generated by self heating must be considered and eliminated. Self heating can be reduced by reducing the measuring current of the detector.
Immersion and probe rod conduction error
When the RTD temperature sensor is only partially immersed in the measured variable, probe rod guide may occur. In general, your minimum immersion depth should not be less than four times the length of the detector or sensing junction.
If the immersion depth is small, the probe rod lead error will occur, which is the effect of heat transfer from or to the measured variable through the rod or sheath. For example, if the sensor sheath is hotter than the measured variable at the ambient temperature, it will be transferred to the variable creating the reading uncertainty.
The conduction effect of the probe rod can be reduced by increasing the immersion length, reducing the wall thickness of the sheath or changing the sheath material.
Dry conduction errors most often occur in laboratory conditions; However, it must be pointed out that they may lead to major mistakes in other industries.
As a rule of thumb, RTD temperature sensors should be immersed 4 times the length of the element. (Flat film elements are usually 2-3 mm, while wound elements are about 15 mm or more).
Measuring current
It is generally believed that in most applications, the Pt100 temperature sensor should have a measuring current of 1mA, but in order to reduce the self heating effect in low temperature applications where accuracy is crucial, 0.5mA should be used.
Some applications do require higher measuring current. Many detectors are often used at 10mA, which has little impact on performance and service life.
Long term stability and repeatability
RTD temperature sensor is famous for its excellent stability and repeatability; However, sensor structure, measurement environment and extreme temperatures can affect long-term stability.
As a guide, it is estimated that in most applications, assuming the temperature is as high as 450 ° C without extreme vibration or improper treatment, the annual drift of RTD temperature sensor should not exceed ± 0.02 ° C.
Repeatability will be affected only if the same thermal conditions cannot be reached or the same RTD temperature sensors have different structures.
As you can see, there are many factors to consider when selecting the appropriate RTD temperature sensor for your application. If you want to further discuss your application or place an order, please call or email 18717811268 sales@weilianchina.com

 RTD temperature sensor accuracy
RTD temperature sensor accuracy