 Six Common Causes of Thermocouple Temperature Measurement Error
Six Common Causes of Thermocouple Temperature Measurement ErrorThermocouple temperature sensor has become one of the most popular temperature measuring instruments in industrial applications due to its versatility and ease of use. However, measurement errors may occur. This article discusses the six most common causes of thermocouple errors.
Thermocouple is a robust temperature measurement equipment, and its accuracy is sufficient to meet the needs of many industrial and scientific applications. Compared with other temperature measurement technologies, thermocouples are relatively cheap and are valued for their ability to measure a wide range of temperatures: from – 200 ° to+1250 ° C.
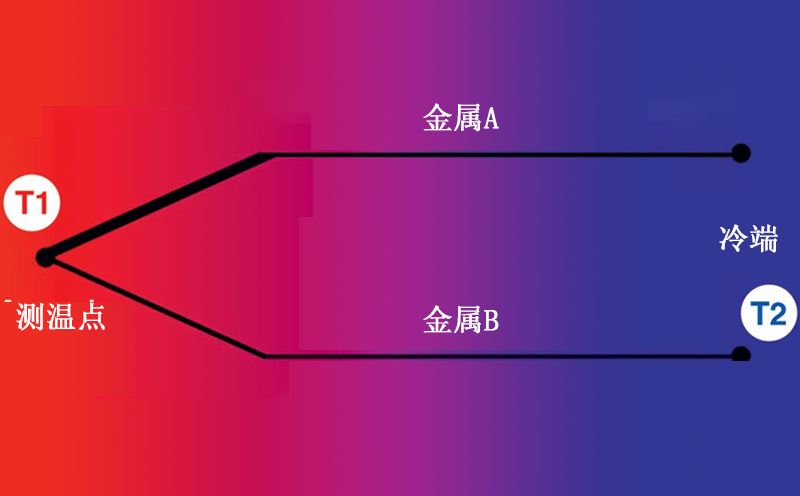
Thermocouple temperature sensors measure temperature differences, not absolute temperatures. Two wires, each made of different metals, are connected at the tip. This is a measuring knot. At the other end, the wire is connected to an object of known temperature, called a reference junction. Thermocouples work by measuring the voltage difference between two nodes, which is explained by the Seebeck effect. The measured voltage is converted into a temperature unit, and the temperature reading is displayed on the device or transmitted to a remote location.
Although the thermocouple is reliable, temperature measurement errors may occur due to various reasons. The following are the six most common causes of thermocouple measurement errors, and how to correct them:
1. Select the wrong type of thermocouple on the transmitter
If the wrong thermocouple type is selected when inputting settings into the transmitter during installation, you may experience problems. This is a common mistake because there are many types of thermocouples - Types K, J, N, E, T, R, S, and B - each with a different range, accuracy, and electrical output.
Solution: Almost all thermocouples are color coded by type, so you usually only need to confirm the color of the thermocouple sheath and match the settings on the transmitter.
2. Problems related to thermocouple extension wire
If the polarity of the thermocouple temperature sensor lead is reversed accidentally, the measured temperature will be incorrect due to the temperature difference between the two ends of the lead. This problem is understandable, because red is the common color of positive charge, and the red line in thermocouple cable usually contains negative signal. This coloring is ANSI standard for thermocouples, but it is not what most people expect.
Solution: Check the connection carefully and replace the thermocouple lead if necessary.
3. Inherent variation of alloy
No two batches of wires are identical. Because the alloy percentage is slightly different in each manufacturing process, some errors in thermocouple accuracy are inevitable. The actual temperature error of the standard thermocouple at the measuring node is within about 1%, which is accurate enough for most applications.
Solution: Ordering thermocouples with special limit wires can double the accuracy. These wires are manufactured with the highest tolerances to ensure as little impurities as possible and maximum alloy proportion consistency.
4. Temperature change around the reference junction connection
Since thermocouples measure temperature differences, any temperature fluctuations around a reference junction (cold junction) with a known temperature will result in incorrect temperature readings.
Solution: Make sure there is no fan or other cooling or heating source near the reference junction. Simple insulation also protects the joint from extreme temperatures.
5. Thermocouples are grounded at multiple locations
Thermocouples shall be grounded at one location only. If it is grounded at multiple locations, a "ground loop" can be created by current flowing from one ground through the thermocouple to another. This may cause electromagnetic fields, which may lead to problems related to radio frequency interference, thus affecting the measurement accuracy.
Solution: Ground the transmitter (connector) or controller/recorder, but not at the same time. Transmitters selected to have internal isolation between input, output, and ground usually provide sufficient isolation to eliminate ground loops. Loop isolators can also be used and can be placed in loop wiring circuits to prevent this.
6. Thermocouple stability
Although thermocouples are reliable temperature measuring devices, they do drift with time. The maximum exposure temperature, cycle measurement, and cycle frequency affect metallurgy, resulting in drift, usually downward. Unfortunately, this drift cannot be predicted, but errors of 1-5 ° C are common.
Solution: The only solution is to replace the thermocouple regularly according to the user's experience.
Tel./WeChat 18717811268 Huang Gong sales@weilianchina.com



 Six Common Causes of Thermocouple Temperature Measurement Error
Six Common Causes of Thermocouple Temperature Measurement Error


