
 Thermal resistance temperature sensor assembly
Thermal resistance temperature sensor assembly
Resistance temperature detector (RTD) is a kind of temperature sensor, which uses the principle that the resistance of metal changes with temperature to measure temperature.
In practice, the current is transmitted through a piece of metal (RTD element or resistor) located near the area where the temperature is to be measured.
Then measure the resistance value of RTD element through the instrument. Then, according to the known resistance characteristics of RTD elements, the resistance value is related to the temperature.
Thermal resistance assembly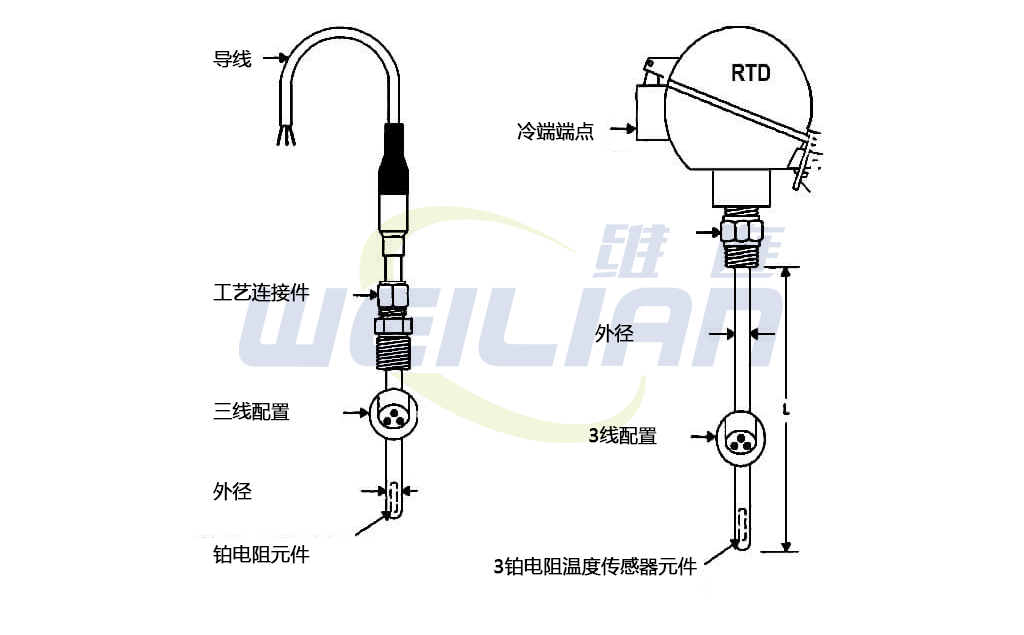
Platinum resistance thermometer is an electric thermometer that uses high purity platinum wire resistance to change with temperature. This change is predictable and can be measured accurately.
They are very sensitive and can be measured at more than one thousandth of 1 ° C using precision equipment. The temperature coefficient defines the degree to which the resistance changes with temperature, in ohms/º C.
The greater the temperature coefficient, the greater the resistance change for a given temperature change. Similarly, as the temperature of the RTD temperature sensor resistance element increases, the resistance measured in ohms (Ω) will also increase. RTD elements are usually specified based on their resistance in ohms at zero degrees Celsius (0 ° C).
The most common RTD specification is 100 Ω, which means that the RTD element should have a resistance of 100 Ω at 0 ° C.
RTDs are usually quite linear, but the temperature coefficient does change over the operating range. As an indication, the temperature coefficient of platinum averages 0.00385 in the range of 0 to 100 º C, but varies about 2% in the same range.
What is? PT100、PT500、PT1000
They are all types of RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) sensors made of platinum. The Pt100 Wendy sensor has a resistance of 100 ohms at 0 ° C and is by far the most common type of RTD sensor.
The PT500 temperature sensor has a resistance of 500 ohms at 0 ℃ and the Pt1000 temperature sensor has a resistance of 1000 ohms at 0 ℃.
These sensors are usually installed in some type of protective sleeve or mounting piece to form probes, which are usually called PRT (platinum resistance thermometer) or RTD probes.
Advantages and limitations of RTD temperature sensor
RTD temperature sensor is one of the most accurate temperature sensors. It not only provides good accuracy, but also provides excellent stability and repeatability. RTD is also relatively unaffected by electrical noise, so it is very suitable for temperature measurement in industrial environments, especially around motors, generators and other high-voltage equipment.
RTDs in industrial applications are rarely used above 660 ° C. At temperatures higher than 660 ° C, it becomes increasingly difficult to prevent platinum from being contaminated by impurities in the thermometer metal sheath.
2-wire, 3-wire, or 4-wire RTD temperature sensors?
A simple rule of thumb is that the more wires in an RTD, the higher the accuracy. reference resources Description of RTD temperature sensor wiring configuration with 2-wire, 3-wire or 4-wire RTD.
What are the common components of RTD temperature sensors?
RTD platinum resistance element:
This is the actual temperature sensing part of the RTD. The length of the element ranges from 1/8 "to 3". There are many choices. The standard temperature coefficient is 0.00385 alpha, and the standard resistance at 0 ° C is 100 Ω.
Outer diameter of thermal resistance:
The most common outside diameter is 1/4 inch internationally and 6 mm (. 236 inch) in other applications. However, the outside diameter ranges from 0.063 "to 0.500"
Pipe material of RTD temperature sensor:
316 stainless steel is typically used for components up to 500 ° F. Above 500 ° F Inconel 600 is recommended.
RTD temperature sensor process connection:
Process connection fittings include all standard fittings used with thermocouples (i.e. compression, welding, spring loading, etc.).
Wiring configuration of RTD temperature sensor:
RTD temperature sensors are available in 2, 3, and 4 wire configurations. The 3-wire configuration is the most common industrial application. Teflon and fiberglass are standard wire insulation materials.
Teflon is moisture resistant and can be used at temperatures up to 400 ° F. Fiberglass can be used at temperatures up to 1000 ° F.
RTD cold termination:
RTD can terminate plugs, bare wires, terminal heads and any reference junction common to thermocouples at the cold end.

