 Calculate the temperature coefficient of RTD temperature sensor
Calculate the temperature coefficient of RTD temperature sensor
RTD temperature sensor is based on the principle that metal resistance increases with temperature. The resistance temperature coefficient of is resistance temperature detector (TCR) (with α It is generally defined as the average resistance change o per degree Celsius within the range divided by the resistance of RTD temperature sensor R at 0 ℃ to 100 ℃, which is 0 ° C.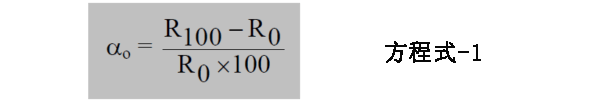
where,
Rtd resistance (ohms) at R 0=0 ° C, and
Rtd resistance at R 100=100 ° C (ohms),
Note: Here we only discuss RTD PT100. Temperature sensor
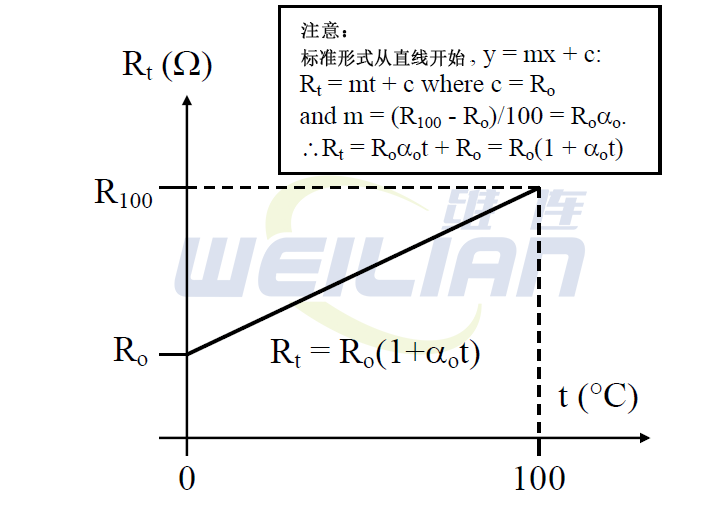
As the first approximation, the relationship between resistance and temperature can be expressed as (see Figure 2):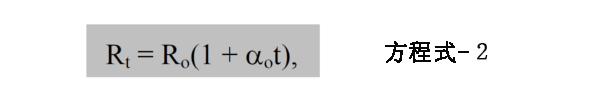
Where R t=resistance of rtd at temperature t (ohms),
Rtd resistance (ohms) at R o=0 ° C, and
α O=Resistance Temperature Coefficient (TCR) at 0 ° C (per ° C)
example
Platinum RTD PT100 is 100 Ω at 0 ° C and 139.1 Ω at 100 ° C.
Calculate RTD resistance at 50 ° C.
Calculate TCR of platinum.
Calculate the temperature when the resistance is 110 Ω.
Calculate the temperature coefficient of RTD PT100
From Equation - 1:
Calculate the temperature coefficient of RTD PT100
Calculate RTD resistance at 50 ° C
From Equation - 2:
R 50 = R o (1 + α t) = 100(1 + 0.00391 × 50) = 119.55Ω
Calculate the temperature when the resistance is 110 ohms
From Equation - 2:
Rt = Ro(1 + α t) ⇒ 110 = 100(1 + 0.00391t)
Rt =1 + 0.00391t = 1.1 ⇒ 0.00391t = 0.1 ⇒ t = 25.58 °C。

