
Temperature controller working principle
The thermostat is a device that maintains the required temperature in the refrigerator, air conditioning, iron and other systems and many devices.
The working principle of the thermostat is the thermal expansion principle of solid materials.
Dual metal chip temperature controller
Traditional thermostats have two different metal bolts fixed together to form a so -called dual metal bar (or dual metal bar). The strip acts as a bridge in the circuit connected to the heating system. Under normal circumstances, the "bridge has been closed", the strip is charged through the circuit, and the heating is turned on. When the steel belt becomes hot, one of the metals expand more than the other metal, so the entire steel band will be slightly bent. In the end, it was bent too hard to disconnect the circuit. "The bridge rises", the electricity is disconnected immediately, the heating is powered off, and the room begins to cool down.
But what will happen next? As the room cools, the strip is also cooled and bent back to the original shape. Sooner or later, it will return to the circuit and flow the current again, so heating will be opened again. By adjusting the temperature scale, you can change the temperature of the circuit to turn on and off. Because the expansion and contraction of the metal strip takes some time, heating is not continuously opened and closed every few seconds, which will be meaningless (and very annoying); according to your home insulation and the coldness of the outdoor, It may take an hour or longer after the thermostat is closed.
How to open and close the dual metal thermostat
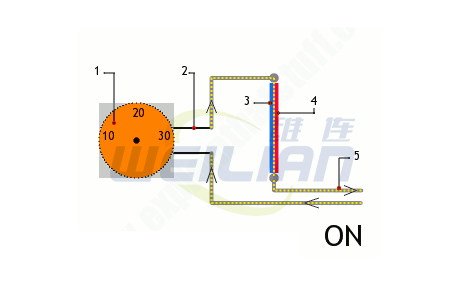
1. The external scale disk allows you to set the temperature of the thermostat to open and close.
2. The dial is connected to the temperature sensor (dual metal bars, which shows red and blue) through the circuit.
3. Dual -metal ("dual metal") strips are made of two separate metal bars: a piece of brass (blue) fixed on a piece of iron (red) with bolts.
4. When the iron becomes hot, the expansion of the iron is smaller than brass, so as the temperature rises, the dual metal strips are bent inward.
5. A dual -metal strip formation circuit (gray path). When the strip is cooled, it is straight, so it acts as a bridge that can pass the current. The circuit is turned on and the heating is the same. When the temperature rises, it will bend and disconnect the circuit, so there is no current to flow. The circuit is now closed.

