 Aliatic Q & A
Aliatic Q & A
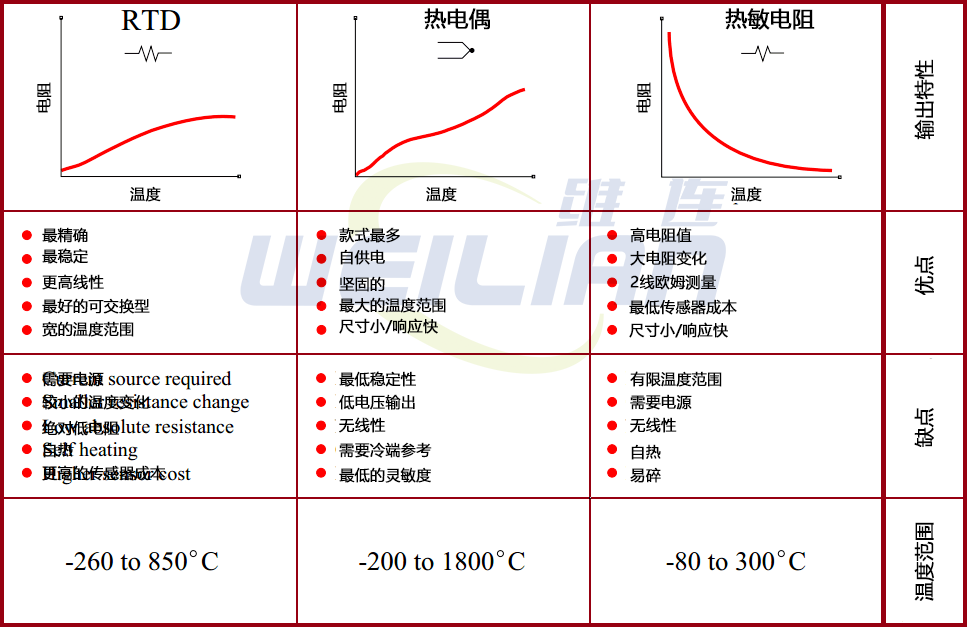
Comparison of thermocouple, RTD and thermal resistance?
What is a thermocouple?
Thermocouple is a sensor for measuring temperature. The thermocouple is composed of two lines made of different metals. The wire leg is welded together at one end to form a connection point.
The node is where the temperature measures. When the temperature changes, the voltage is generated. You can then use the thermocouple reference table (link) to explain the voltage to calculate the temperature.
There are many types of thermocouples. Each type has its unique characteristics in terms of temperature range, durability, vibration resistance, chemical resistance and application compatibility.
J, K, T and E are "cheap metals" thermocouple, which is the most common thermocouple type. R, S and B thermocouples are "precious metals" thermocouples for high temperature applications (see the temperature range of thermocouple.
Thermocouple is used for many industries, science and OEM applications. They can be found in almost all industrial markets: power generation, petroleum/natural gas, pharmaceutical, biotechnology, cement, papermaking and pulp, etc. Thermocouple is also used for daily electrical appliances such as stoves, furnaces and baked noodles.
The thermocouple is usually selected because they have low cost, high temperature limit, and wide temperature and durability.
What is the cold (reference) node of the thermocouple?
The cold end or reference end is the end of the thermocouple of the reference point.
The temperature difference between the thermocouple measurement between the two nodes. They do not measure the actual temperature. The sensing node is a place where the thermoelectric puppet welding (or connecting in other ways) is located at a point that requires temperature.
Another node is usually located where it is connected to the instrument (measuring device or transmitter). This is called the cold end or reference end.
The hemcove meter and mathematical formulas are based on a cold end temperature of 0 ° C. In order to determine the actual temperature, the instrument must "adjust" the difference between the ambient temperature and 0 ° C. This adjustment is called cold -end compensation.
The thermocouple of ground or not ground?
When the sensing node (physical and electrical) is connected to the metal case, the thermocouple is called "grounding".
There are advantages and disadvantages, but the thermocouples that are usually not grounded are more desirable, and the slower response time is acceptable.
What is the difference between thermocouple and RTD temperature sensor?
Temperature range
First, consider the difference in temperature range. The precious metal thermocouple can reach 3,100 F, while the standard RTD limit is 600 F, and the limit of the RTD of the extended range is 1,100 F.
Cost
Ordinary valve stem thermocouples are 2 to 3 times cheaper than ordinary valve stem RTDs.
The thermoelectric puppet head component is about 50%cheaper than the equivalent RTD header.
Accuracy, linearity and stability
As a general rule, RTD is more accurate than thermocouple. This is especially in the lower temperature range.
RTD is also more stable and more linear than thermocouple. If accuracy, linearity and stability are your main focus, and your application is within the temperature limit range of RTD, use RTD.
Durability
In the sensor industry, RTD is widely considered to be sensors with poor durability compared with the thermocouple.
Response time
RTD cannot be grounded. Therefore, their response time is slower than the geothermal power puppet.
In addition, thermocouple can be placed in the shenthes with a diameter of less than RTD.
Smaller sheet diameter increases the response time. For example, a grounded heat puppet with a diameter of 1/16 inches.
The sheath sheath will have a faster response time than the RTD in the diameter.
What are the types of thermocouple junction?
grounded thermocouple:
This is the most common connection style. When the thermocouple line and the protective cover are welded together to form a node at the tip of the probe, the thermocouple is grounded.
The grounded thermocouple has a very good response time, because the thermocouple puppet is directly contacted with the protective cover, allowing heat to be easily passed.
A disadvantage of a grounded thermocouple is that the thermocouple is more vulnerable to electrical interference. This is because the sheets often come into contact with the surrounding areas, which provides a path for interference.
Undumerical geothermal puppet:
When the thermocouple line is welded together but they are insulated from the sheet, the thermocouple is not grounded.
The wire is usually separated from the mineral insulation layer.
exposed heat puppets (or "naked wire thermocouple"):
When the thermocouple line is welded together and inserted directly, the thermocouple is exposed.
The response time is very fast, but the exposed thermoelectric puppet line is more likely to corrode and degenerate. Unless your application needs to be exposed, this style is not recommended.
Not ground and not common:
The non -ground non -Putong thermocouple is composed of dual -thermal electric puppets insulated with the sheath, and each component insulated each other.
mi cable ?
MI (mineral insulation) cables are used to inside each other with the thermocouple line and inside the metal sheath around them.
Mi cables have two (or four dual -time hours) thermocouple lines extend down from the middle of the tube.
Then fill the tube magnesium powder and compact to ensure the correct insulation and separation of the wire.
MI cables help protect the thermocouple line from corrosion and electrical interference.
What is the difference between the thermocouple sheath?
● 316SS (stainless steel): This is the most common sheath material. It is relatively corrosion -resistant and cost -effective.
● 304SS: This sheath is not as resistant to corrosion as 316SS. The cost difference between 316ss and 304SS is nominal.
● Inconel (registered trademark) 600: This material is recommended for strong corrosive environment.
What does the color of thermoelectric puppet line represent?
The thermocouple can be identified by the color of its wire insulation layer.
For example, internationally, there is a red line and a white wire in the J -type thermospace, usually with brown skin.
There is also a red line and a white line in the J -type extension, but it has a black outer condom.
Generally speaking, the red line of the thermocouple or extension line is a negative electrode, and the positive line is coded according to the type of thermocouple.
Different countries use different color code.
What is the difference between thermocouple cable and extension?
Thermocouple -level wire is used to create armocuel probe.
Thermocouple -level wire is usually used to connect and the inside of the valve shean cover. This is because thermocouple -class wire has better accuracy specifications than extended wires.
extension line is a cheaper low -level line. It is used to extend the signal from the thermocouple probe to the control system or digital display.
Because of the use of lower -level metals, extended rated wires are more economical.
The extension -level wire should not be used in the process itself, nor should it be regarded as a standard -grade wire.
What is the Syberk effect?
When the two different metal or metal alloys are connected at one end (hot connection point), a thermal power puppet is formed.
If there is a temperature difference between the thermal end and the opening side, the thermal electromotive force (thermal voltage) will be generated in the thermocouple. This is also called the Syberg effect.
What is CJC?
Thermocouple measurement always requires information from the connection line (thermal end) and the opening side (cold end). The cold knot is also called the reference point.
The changes in the temperature of the reference point are compensated by CJC measurement (cold end compensation).
Temperature transmitter CJC measurement can be a measurement resistor that can be an internal function or integrated in the connector.
If the reference point is away from the transmitter, it must be measured separately and connect it as a compensation signal to the transmitter.
What is compensation cable and extended cable?
compensation cable is a thermocouple measurement circuit cable, which uses the letter C to identify (such as KC -type cable KC).
The wires of the compensation cable have the same electrical characteristics as the hotline of the TC sensor, but the materials are different.
Compensation cables are more cost -effective than extended cables, but the maximum ambient temperature is low, about 100… 200 ° C, depending on the insulation material.
Extending cable is a kind of armocouple cable that uses the letter X identification (such as K -type cable KX). The wiring of the extended line is exactly the same as the hot wire material of the TC sensor.
These cables can even reach the same ambient temperature as thermocouple.
What is a trace heating/sensor?
Accompaniment is a term that is usually used to keep the pipeline and connection equipment from freezing.
The important role of accompaniment is to maintain the temperature and flow of the material flowing through the pipeline.
The most common implementation method of tracking heating is electrical, which provides good adjustable.
However, in order to accurately control and adjust, accurate temperature data is needed.
For these applications, we have designed a high -quality heat -with heat sensor. These sensors have been launched for many years and are also applicable to explosion -proof applications.
What size hot suit is suitable for my application?
According to your system design, you need to understand:
● Work temperature (° C)
● Work pressure (BAR), Birong (m3 /kg)
● Speed (meter /second)
After confirming this, you can refer to the ASME standard PTC 19.3 TW-2010 thermal suite part, which is calculated through the well design.
The following are some basic rules you can follow*:
● Usually, higher flow velocity requires shorter heat suite.
● Ensure that thermal tube material is compatible with the medium immersed in it.
● Economic welding hot sleeve can be used for low flow applications, such as some HVAC cooler pipelines (usually less than 1-3 feet/s).
● cone -shaped thermal sleeve is usually more suitable for high flow rates than stairs (reducing tip) heat sucks.
What is a high temperature meter and explain its working principle?
High temperature meter is a non -contact device that can intercept and measure heat radiation.
The process of no contact with the radiation body is called high temperature measurement. The device can be used to determine the temperature on the surface of the object.
High temperaturemeter work strictly in accordance with the principle of black body radiation. Here, the target's launcher plays an important role because it determines the brightness of the target in the high temperaturemeter.
Because of its high accuracy, speed, economy and specific advantages, it is widely used as standard procedures in many industrial applications.
The current application:
● Optical systems from object collection of visible light and infrared energy and focus them on the detector.
● The detector receives a photon energy from the optical system and converts it into a electrical signal to drive or control the unit.
Thermocouple measurement node
When the maximum sensitivity and the fastest response are required, it is recommended to use exposed (measurement) to measure the non -corrosive gas temperature of flowing or static.
Although the thermal response is slow, the insulation junction is more suitable for corrosive media.
In some applications of connecting multiple thermocouples to some related instruments, insulation may be essential to avoid bruises in the measurement circuit. If there is no specification, this is the standard.
grounding (grounding) joints are also applicable to corrosive media and high -pressure applications.
It provides a faster response and exposure nodes that are not provided than the insulation node.
thermocouple standard
● ASTM E 235: Armocouple K -type and N standard specifications for nuclear or other high -reliability applications.
● ASTM E 839: Standard testing methods for thermal dodks and sheath thermocouple materials.
● ASTM E 220: Testing method of calibrating thermocouple through comparative technical calibration
● ASTM E 230: Specifications and temperature-EMF tables of standardized thermocouple.
● ASTM E 585: Standard specifications of compact MI, MS, and cheap metal thermocouple cable.
● ASTM E 608: Standard specifications of compacting MI, MS, and cheap metal heat puppets.
● ASTM E 696: Standard specifications of tungsten puppets.
● ASTM E 1652: The standard specifications of magnesium oxide and aluminum oxide powder and crushed insulators for metal sheath PRT, cheap metal hot electric puppets and precious metal thermocouples.
● IS 12579: Specifications for cheap metal mineral insulation thermostat cables and thermocouples.
● GB/T 1598-2010: Chinese platinum thermocouple standard.
● IEC 584: International standards for thermocouple.
Application of heat suite
Thermal tube provides protection for temperature probe to prevent adverse operating conditions, such as corrosive media, physical shocks (such as clinker in the furnace) and high -pressure gases or liquid.
Their use also allows to quickly and easily replace the probe without the need to "open" the process.
The main application areas are:
● Protective pipes for thermocouple
● Make sure the integrity in high -pressure applications
● Small wells for low -voltage applications
● Straight wells for corrosive and corrosive environments
● For applications that need to make rapid response to temperature changes, prefabricated pockets can be equipped with a narrow -cut tip.
All -in -one thermal sleeve pipes are suitable for the highest process load, depending on its design. Therefore, in the petrochemical industry, almost only all -in -one thermocouples are now used.
Thermocouple structure type
There are two most commonly used thermocouple structures.
These are mineral insulation (MI) thermocouple and non -MI thermocouple.
Mineral insulation thermal power puppet:
Magnesium oxide insulation thermocouple is used for many processes and laboratory applications.
They are sturdy and bending, and their high rated temperatures make the MGO thermocouple a popular choice for many temperature measurement applications.
The constructor of the MGO sensor is to put one or more components in a cover cover of the appropriate material and size, and use a loose or crushed magnesium oxide powder or insulator The filled sheath is squeezed or stretched to its final reduction.
Model forging processes produce components with high compact MGO insulation layers, and provide high -agency strength insulation between the components itself and its sheets.
Mineral insulating thermal power puppets are composed of the thermoelectric puppet lines embedded in dense refractory oxide powder, and they are all closed in seamlessly pulled metal shestons (usually stainless steel).
At one end, the core wire and the sheath are welded from the "heat" connector. On the other end, the thermocouple is connected to the "transition" of the extension line, the connector or the connector.
Non -mi thermocouple
Among the non -MI thermocouples, the thermoelectric puppet line either uses ceramic bead insulation, or after ceramic insulation, cover with metal sheaths (usually stainless steel), and provide a form of end connection (such as extended lines, connectors or connections Device).
In this type of structure, when providing protective cover protection, the thermocouple line is not affected by the measurement environment.
Guard materials depend on the measurement environment and usually use stainless steel. Choose different protectives according to the corrosion environment.
This structure does not provide flexibility and cannot be found in small sizes. The mechanical strength is not good.
In non -MI structures, the protective cover can be made from ceramics or metals according to the applicability.
All types of all types of exposure, grounding, and unscated are formed in the MI and non -MI structures.

