
Thermocouple structure
The nails are constructed in two different metal wires connected to a end. When one end of each wire is connected to the measurement instrument, the thermocouple is a sensitive and high -precision measurement device.
The thermocouple can be composed of several different materials. The performance of thermocouple material is usually determined by using the material with platinum.
The most important factor to consider when choosing a pair of materials is the "heat and electricity difference" between the two materials. The significant difference between the two materials will lead to better thermocouple performance.
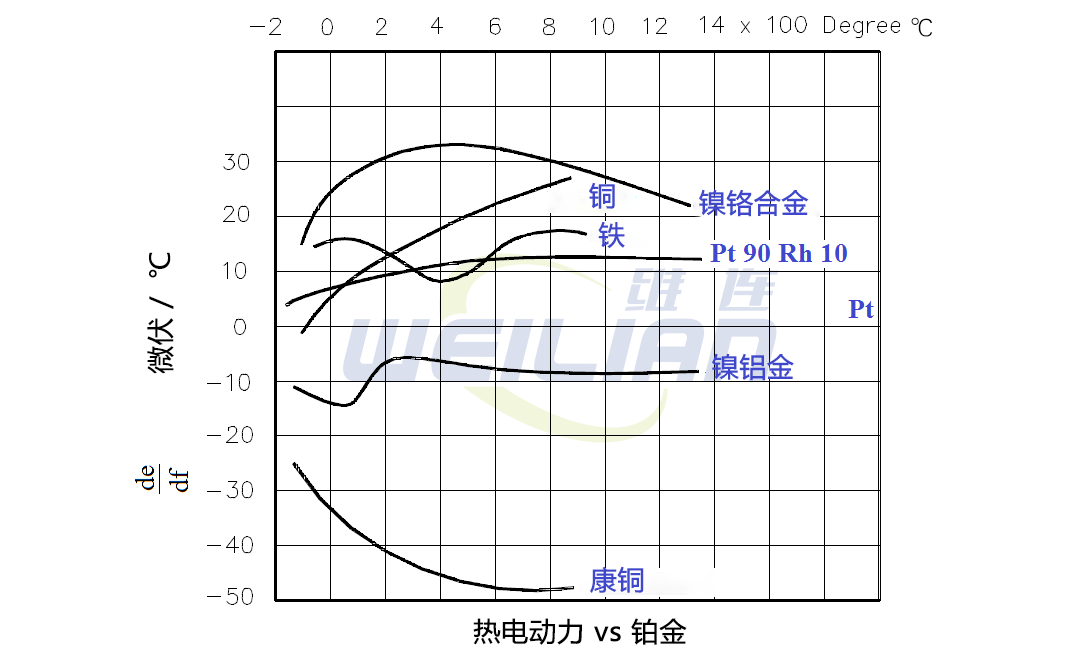
Figure 1 illustrates the characteristics of more commonly used thermocouple materials when using platinum.
In addition to the materials shown in Figure 1, other materials can also be used. For example: Chromel-Constantan is very suitable for temperatures up to 2000 ° F; nickel/nickel-molybdenum sometimes replace Chromel-Alumel; tungsten cymbals are used for temperatures up to 5000 ° F. Some combinations for special applications are chromium white gold, molybdenum-tungsten, tungsten.
Figure 2 shows the internal structure of the typical thermocouple. The leadership of the thermocouple is wrapped in a rigid metal sheath. The measurement knot is usually formed at the bottom of the thermocouple shell. Magnesium oxide surrounds the thermocouple line to prevent the vibration of the fine lines that may damage the fine line and enhance the heat transfer between the measuring knot and the media around the thermocouple.
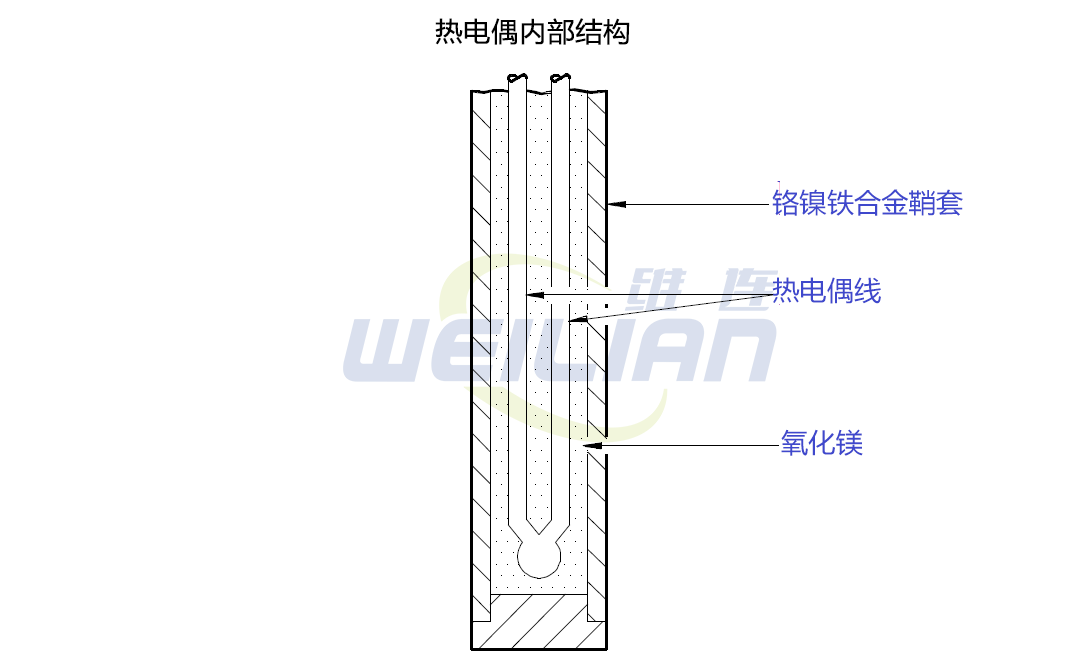
Figure 2 Internal structure of typical thermocouple
Thermocouple operation
When the temperature changes, the thermocouple will cause the current to flow in the circuit where the current is connected. The generated current depends on the temperature difference between the measurement node and the reference node; the characteristics of the two metals used; and the characteristics of the attached circuit. Figure 3 illustrates a simple thermocouple circuit.
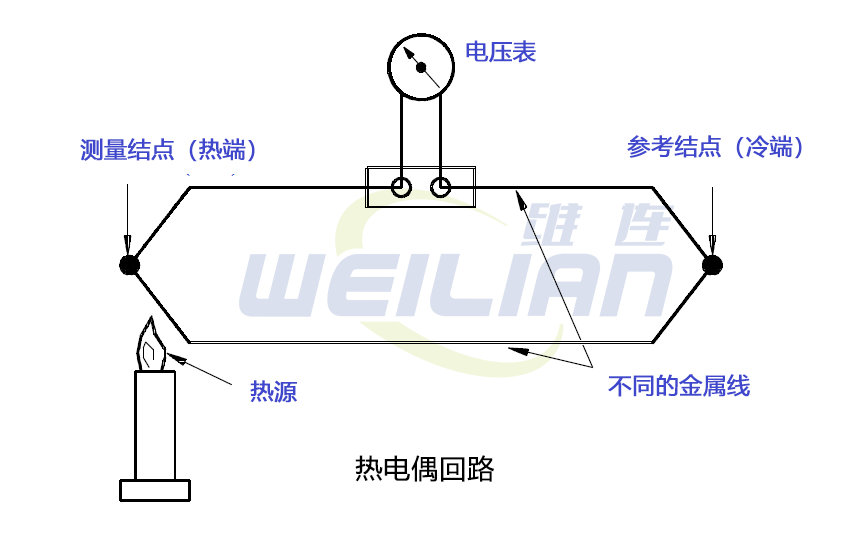
Figure 3 Simple thermocouple circuit
The voltage generated by the measurement knot of heating heat puppet is greater than the voltage at both ends of the reference end. The difference between the two voltages is proportional to the temperature difference, and can be measured on the voltage meter (in the millions). In order to facilitate the use of operators, some voltage meters are set to read the temperature directly by using electronic circuits.
Other applications only provide millivolva reading. In order to convert the millivolva reading to its corresponding temperature, you must refer to the table shown in Figure 4. These forms can be obtained from the thermocouple manufacturer, which lists a series of specific temperatures corresponding to the number of millivolva reading.
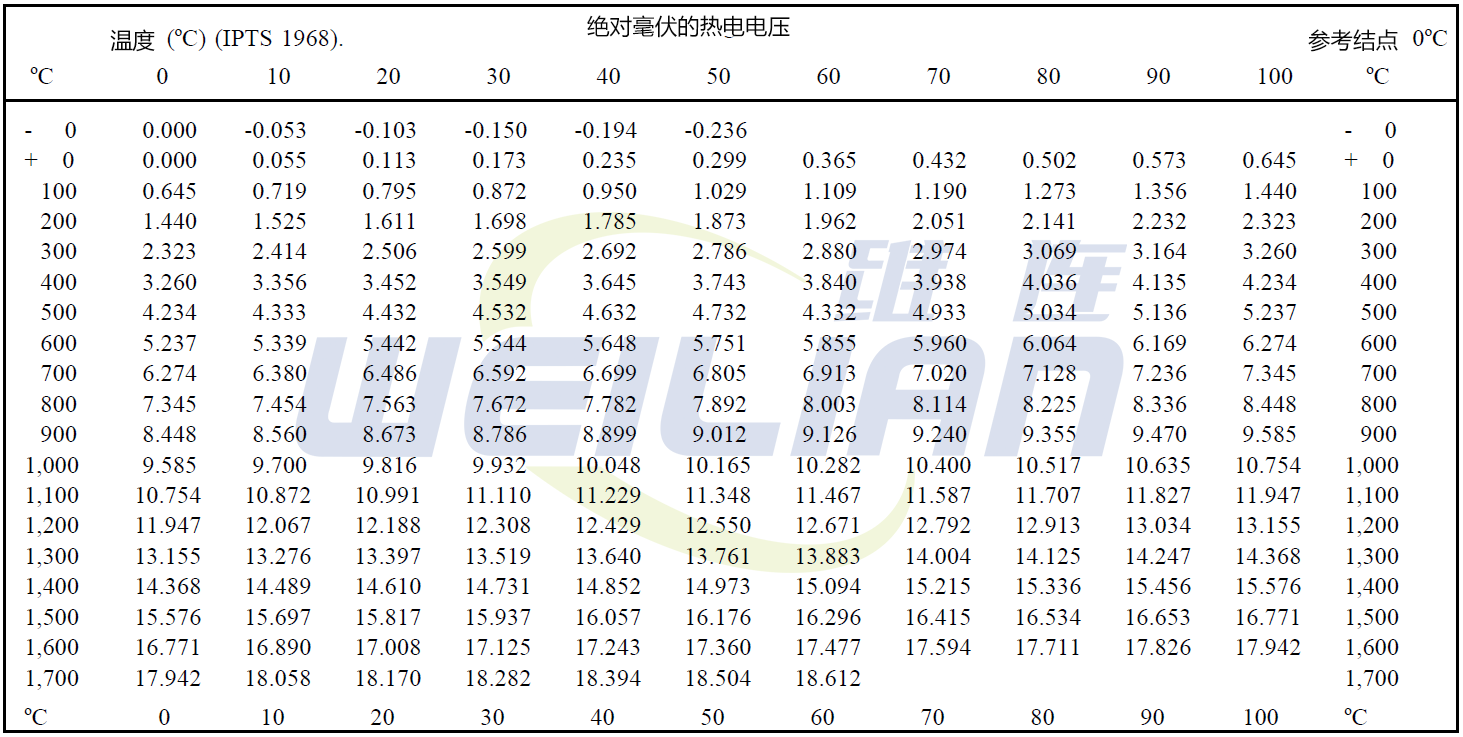
Figure 4 temperature-voltage reference table
Sum up
The summary of the thermocouple is as follows.
● The thermocouple is composed of two different wires that are connected to both ends and wrapped in the metal sheath.
● The other end of each wire is connected to the instrument or measuring circuit.
● The voltage generated by the measurement end of the heating power puppet is greater than the voltage at both ends of the reference end.
● The difference between the difference between the two voltages is proportional to the temperature difference and can be measured on the voltage meter.

