
 Winding resistance
Winding resistance
What is a wire wound resistor?
A 20W 5 ohm ceramic wire wound resistor wound resistor is a passive electronic component that restricts current. The resistance component is an insulating metal wire wrapped around the non -conductive core. The wire has a high resistivity, which is usually made of alloy such as Nichrome or Manganin or manganin. Common magnetic core materials include ceramics, plastics and glass. The line -wound resistor is the oldest resistor type that is still produced today. They can produce very precisely and have excellent characteristics in low resistance and high rated power.
Definition of wire wound resistor
The winding resistor is a resistor, where the wire with a high resistivity is wrapped on the insulating core to provide resistance.

Structure
The structure of the winding resistor has changed a lot. The choice of manufacturing methods and materials depends on the use of the resistor in the circuit. All of them are made by wrap the wires around the magnetic core. The resistance value depends on the resistivity, cross -section and length of the wire. Because these parameters can be accurately controlled, high -precision resistance can be achieved. For high -capacity differences, the measured resistance value is measured to accurately determine the length of the cutting wire. In order to generate high resistance, the line diameter requires very small and the length requires very long. Therefore, wire -wound resistors are mainly produced for lower resistance. For low rated power, use very thin wires. It is important to deal with very fine wires. Any damage may cut off the wire. After wound,
There are also some wire -wound resistors that have a high rated power of 50 W or higher. These resistors have completely different structures. Compared with other types of resistors (such as metal membranes), the wire diameter is relatively large, so it is stronger.
Resistor material
The wire winding resistor is mainly made of alloy because pure metal has a high resistance temperature coefficient (TCR). However, for high temperature, pure metals such as tungsten. The temperature coefficient is the degree of measurement of the degree of resistance with temperature changes. TCR measured PPM/° C. If the maker's rated value of the resistor is 50 PPM/˚C, for the temperature change of 1 ˚C, the resistor of the resistor will not exceed 50 Ω for the demarcation of the grade value per 1 MΩ resistor. Typical alloys used for resistance wires are:
● Copper alloy
● Silver alloy
● Nickel chromium alloy
● Iron chromium alloy
● Iron chromium aluminum alloy
The following table lists the characteristics of the most common alloy.
| Alloy | Material | Element (%) | Resistivity (10 -6 Ω/m) | TCR (10 -3 Ω/°C) | Maximum temperature(°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Constant | 54Cu - 45Ni - 1Mn | 0.485 | 0.2 | 400 |
| Nickel gold | 67Cu - 30Ni - 3Mn | 0.40 | 0.11 | 300 | |
| Manganese copper | 86Cu - 2Ni - 12Mn | 0.442 | 0.02 | 300 | |
| Silver | N.B.W. 109 | 82Ag - 10Mn - 8Sn | 0.55 | 0.0 - 0.04 | |
| N.B.W. 139 | 78Ag - 13Mn - 9Sn | 0.61 | 0.0 - 0.08 | 0 - 150 | |
| N.B.W. 173 | 80Ag - 17Mn - 3Sn | 0.58 | 0.0 - 0.105 | 0 - 200 | |
| Nickel Chromium | Nickel chromium alloy | 77/80Ni - 20Cr - 0/2Mn | 1.105 | 0.17 | 1100/1150 |
| Iron chromium | Chromium nickel iron 1 | 70Ni - 20Cr - 8Fe - 2Mn | 1.11 | 0.9 | 1050/1100 |
| Chromium nickel iron 2 | 63Ni - 15Cr - 20Fe - 2Mn | 1.12 | 0.89 | 1050/1100 | |
| Iron chromium aluminum | Chromium aluminum cobalt heat resistance steel A | 72Fe - 20Cr - 5Al - 3Co | 1.45 | 0.06 | 1300 |
| Saka | 75Fe - 20Cr - 5Al | 1.4 | 0.04 | 1300 | |
| Megpar iron chromium aluminum resistance wire alloys | 65fe -30Cr -5 aluminum | 1.4 | 0.025 | 1350 | |
| Pure Metal | tungsten | 100W (sintering) | 0.0553 | 4.5 | 1500/1700 |
For high -precision measurement applications, the difference between the material and the material of the resistance line and the connection lead may have a negative impact. At the nodes between the materials, changes in temperature will cause a small unnecessary voltage to generate a small end at both ends of the resistor. This is called the thermal power effect.
High -frequency effect; induction and capacitance
There are naturally some parasitic capacitors and inductors of wire -wound resistors. As a result, they will affect the current in the AC circuit. These effects of these parasitic effects are usually unwilling. Compared with AC current, DC current is less affected by parasitic capacitors and self -induction.
Due to the design principle of a wire -wound resistor (basically an inductor), the high -frequency characteristics of these resistors are the worst of all resistors. There are several ways to apply winding, depending on the application of the resistor. In order to reduce these parasitic effects, there are several specialized winding types:
● Double -line winding
● Wrap on the flat roll machine
● Ayrton-Perry Winding
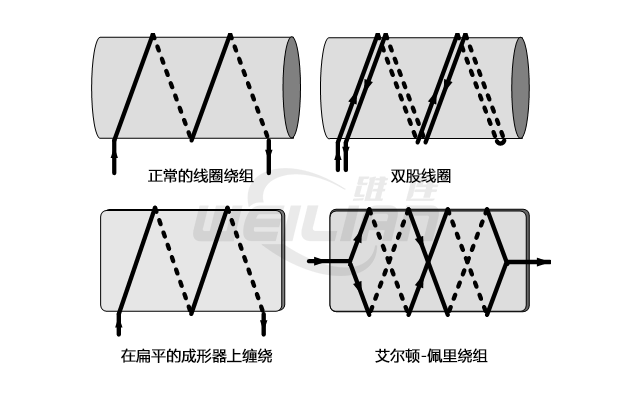
Reduce parasitic winding technology
These types of winding are suitable for measuring equipment and decimal groups. The disadvantages of these methods are difficulty in manufacturing.
The dual -wire winding dual winding is a winding with a double -folding wire into double. The dual line is then wrapped on the substrate material to form a resistor. This winding is very low, but the parasitic capacitance between the wires is very large.
Another way to simply reduce the capacitance generated by the double -line winding on the flat coil is the simple wound on the flat coil. The thinner the card, the closer the line on both sides. They offset each other's magnetic fields, thereby reducing the inductance.
The Ayrton-Perry winding resistor has the Ayrton-Perry winding to require the most stringent circuit. This type of winding is similar to the simple winding on the flat coil frame, but in this case, two opposite windings are applied. The wires with the opposite direction are leaned together to make the winding unwilling to feel. The intersection of the two windows is at the same potential to minimize capacitors.
Type of wire wound resistor
The wire wound resistor can be roughly divided into two categories: precision and power type. They can modify it for current sensors, temperature sensors and potentials. These multi -functional resistors can be used for widespread application.
Precision line around

Precision wire winding high -precision wire windows are usually used for precision audio (AF) attenuations, measured bridges and calibration equipment. The typical value of resistance to tolerance is 0.1% or better. The temperature coefficient of resistance is usually about 5 ppm/° C, which is far better than most metal membrane resistors (about 25 PPM/° C). The stability is also quite good. It runs for a year at a full power rated value, and the value changes to 35 PPM. The temperature rise of these resistors is usually lower than 30 ° C. So they can be coated with epoxy resin materials. In practice, the designer may determine that the resistor needs to be within ± 0.05% of the design value of the specific circuit application. In order to consider aging, TCR and other parameters, the designer may specify the tolerance of ± 0.01%.
Power cord around

The power line winding device wire wound resistor is suitable for very large power applications. The range ranges from 0.5W to 1000W. The power line wound resistor can be classified according to the coating type.
Silicon resin is used for the lowest power consumption level. These are compact resistors, which can withstand the temperature of 300 ° C higher than the ambient temperature.
Another type of coating is enamel. This traditional coating has good insulation performance at low temperatures, but decreases when running at full rated temperature. This attribute makes it less commonly used. The highest working surface temperature can reach 400 ° C. TCR changes between 75 and 200 ppm/° C, and the typical resistance value is within the range of 1 ω to 10 kΩ.
Most power wire windows have ceramic cores and ceramic coatings to protect the winding. Ceramic coatings combine high insulation and physical protection and good heat dissipation. The typical rated power is between 4 and 17 W. The highest surface temperature is about 300 ° C, and TCR changes between 250 and 400 ppm/° C. The resistance value is between 10 kΩ and 22 kΩ. Usually they are manufactured with a leading or horizontal installation.
In order to obtain the highest power consumption value, the wire -wound resistor has an aluminum shell with a wing piece. These fins provide a larger heat dissipation surface area, allowing resistors to process more power without being damaged. These resistors have ceramic core and silicon resin coating, which are packaged in aluminum squeezed parts. The surface is oxidized to maintain a good insulation resistance. The typical rated power of these power winding resistors is 25 to 50 W. This assumes that the resistor will be installed on the metal surface to help dissipate power. When the highest surface temperature is about 300 ° C, when the resistance value is higher than 50 ω, the TCR is lower, which is about 25 ppm/° C. Generally, the lower the resistance value, the higher the TCR.
Potentiometer line around

The potentiometer is usually a wire wound resistor. The potentiometer is a resistor with three terminals. One of them is connected to a mobile contact that can change the size of the resistor. Due to its durable structure, a wire -wound resistor is suitable for potential meters.
Application
Wire -wound resistors are usually used for circuit breakers or as fuses. In order to make a melting resistor, the manufacturer connects a small spring on one end of the resistor. A small amount of solder will fix this spring. If the current and calories of the resistor are high enough, the solder will melt, and the spring will pop up and turn on the circuit. Due to its high power capacity, wire -wound resistors are common in circuit breakers. It can be used as a component in large circuit breaker equipment, and can also be used as the circuit breaker itself.
When the melting wire window is used for high -power applications, they are usually marked as circuit breakers. You can make a wire winding resistor to provide high power and high accuracy. These potential meters are usually used in stereo systems because their accuracy and high -power applications (such as converters and TVs). The wire wound resistor can also be used as a temperature sensor. In this case, use metals with a positive temperature coefficient. This means that the resistance rises as the metal temperature rises. This changes can be measured and the temperature value is converted back to the temperature value.
The natural induction effect of enhanced wire windows can allow these resistors to use as current sensors. Sensor is determined by the inductance of the device and the current flowing through it. The current sensing device is measured and converted to the current reading. These are used for high current conditions, and they need to correct them before the circuit breaker. Large cooling water pumps and freezers are examples of such applications.

