
 How to eliminate the lead resistance of 3-wire RTD temperature sensor?
How to eliminate the lead resistance of 3-wire RTD temperature sensor?
Today I want to share an article about how to eliminate/reduce the lead resistance of a 3-wire RTD temperature sensor compared to a 2-wire RTD temperature sensor. In addition, we will discuss the influence of ambient temperature on RTD measurement.
The following questions let us clearly understand the influence of 3-wire RTD temperature sensor and ambient temperature on RTD temperature sensor temperature measurement.
A Wheatstone bridge, with 100 Ω fixed resistors R1, R2 and R3, and a platinum resistance RT for measuring temperature at 100 ℃, powered from a 10 V battery, with 139.1 Ω resistance at 100 ° C.
The thermometer is connected to the bridge by a lead wire with a resistance Rlead of 10 Ω at 20 ° C, and the thermometer has been correctly calibrated for an ambient temperature of 20 ° C.
Assume that when the ambient temperature rises to 30 ° C, the lead resistance becomes 11 Ω.
Calculate the temperature error introduced when the ambient temperature is 30 ℃
a) Two line method sum
b) Three line method.
We understand RTD temperature sensor resistance (RT) and bridge resistance values. Calculate I1, I2, and then calculate the bridge voltage. The bridge voltage will be used to find the equivalent temperature. Therefore, use 2-wire and 3-wire RTD temperature sensors to measure and compare bridge voltages in the same scenario at different ambient temperatures.
2-wire RTD
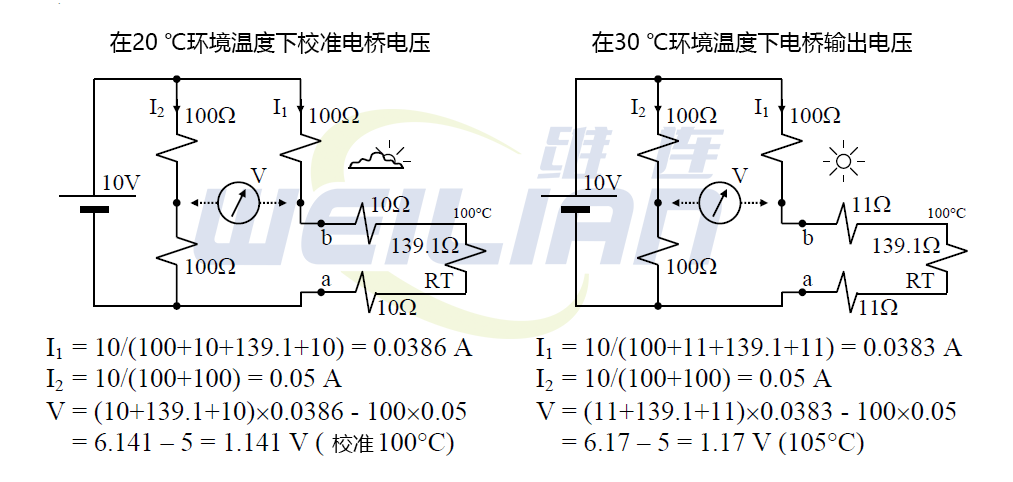
Therefore, if the bridge is correctly calibrated at an ambient temperature of 20 ° C, an error of 0.029 V will occur when the ambient temperature rises to 30 ° C.
Therefore, its reading is not 100 ° C, but about 105 ° C, with an error of 5 ° C or 5%.
3-wire RTD
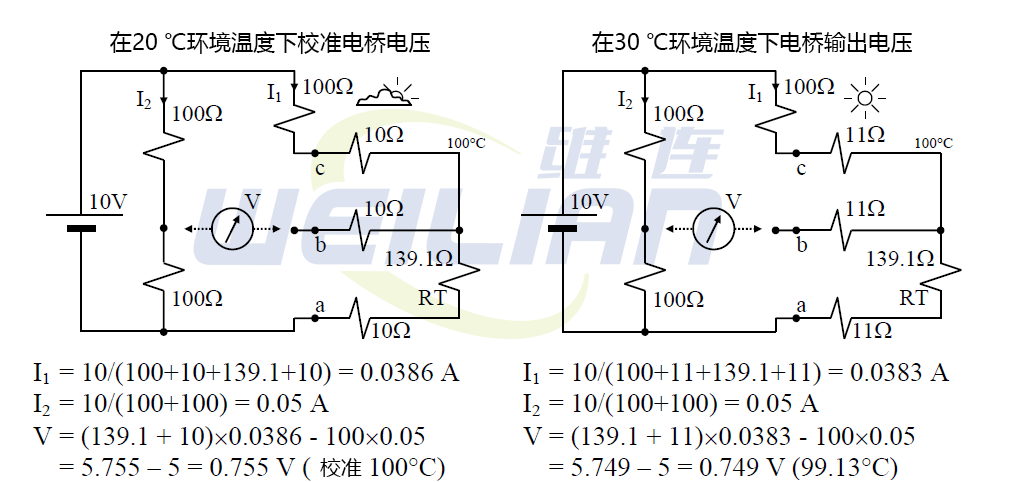
Therefore, the error of 0.006 V will only occur when measuring with the three wire method. If the thermometer (RTD) is correctly calibrated to read 100 ° C at an ambient temperature of 20 ° C, then if the ambient temperature rises to 30 ° C, the reading of 0.749 V will correspond to no rise in the ambient temperature of 138.76 Ω of RT, or for temperature, 99.13 ° C, the error is 0.87 ° C or 0.87%. This is obviously a significant improvement on the two line method.
So we usually prefer 3-wire RTD temperature sensors to 2-wire ones. We use 4-wire RTD temperature sensors for more accurate temperature measurements (rarely used).

