
How to use resistance to convert current to voltage?
In this article, we will discuss how to use the resistor to convert the current to voltage, such as the conversion of 0-20 mA to 0-10 VDC, the conversion of 4-20 mA to 2-10 VDC, 0-20 mA to 0-5 VDC conversion conversion.
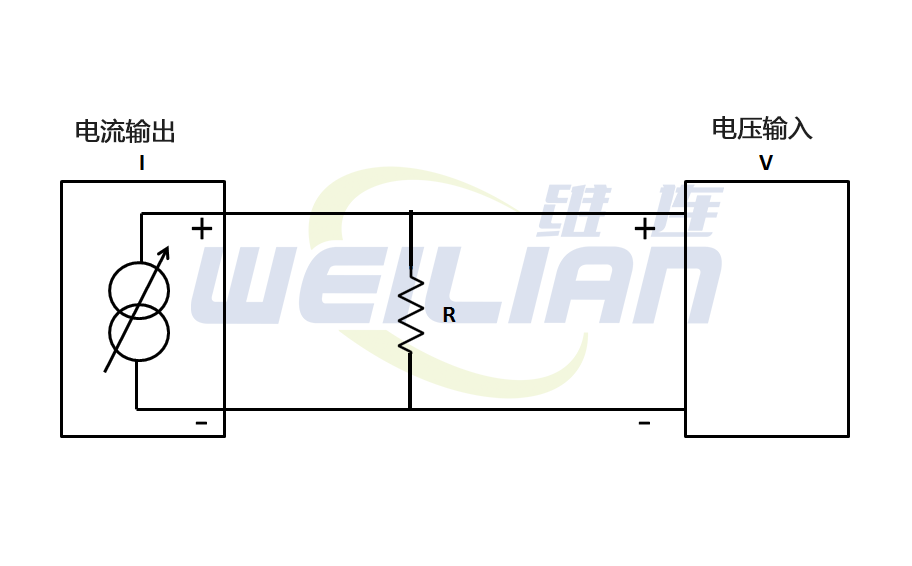
Convert the current to voltage
The 0-20 MA signal using the device that measures only voltage input is very simple. If the available voltage input module will accept the 0-10 VDC signal, but the 0-20MA signal may not be accepted directly.
Basically, Ohm's law is used to calculate the resistance value in order to convert the 0-20mA signal to voltage.
Example: The conversion of 0-20 ma to 0-10 VDC
Ohm's Law pointed out: R = V/i is voltage, i is current, R is resistance
R = 10V /0.020A = 500 ohm
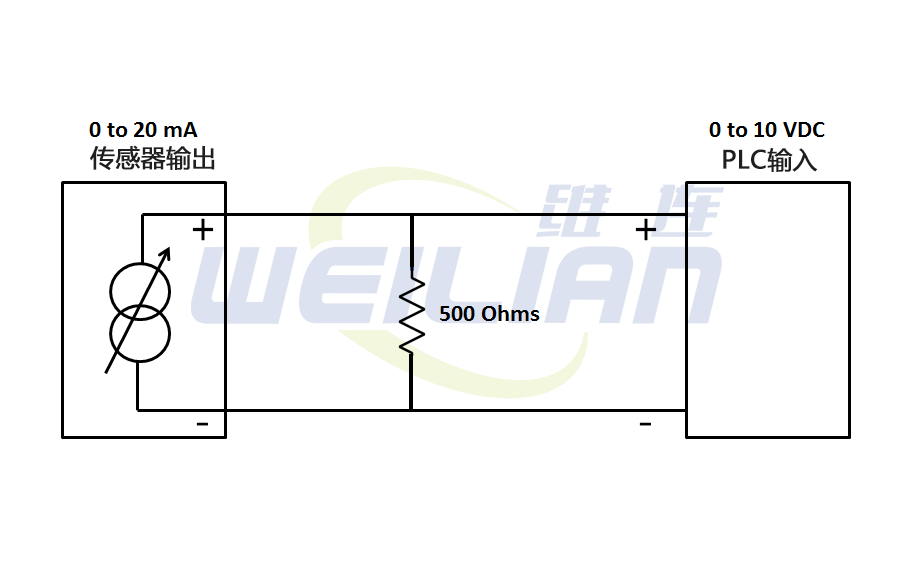
V = I*R = 0*500 = 0V
V = I*R = 0.020*500 = 10V
Example: 4-20 mA to 2-10 VDC conversion
Ohm's Law pointed out: R = V/i is voltage, i is current, R is resistance
R = 10V /0.020A = 500 ohm
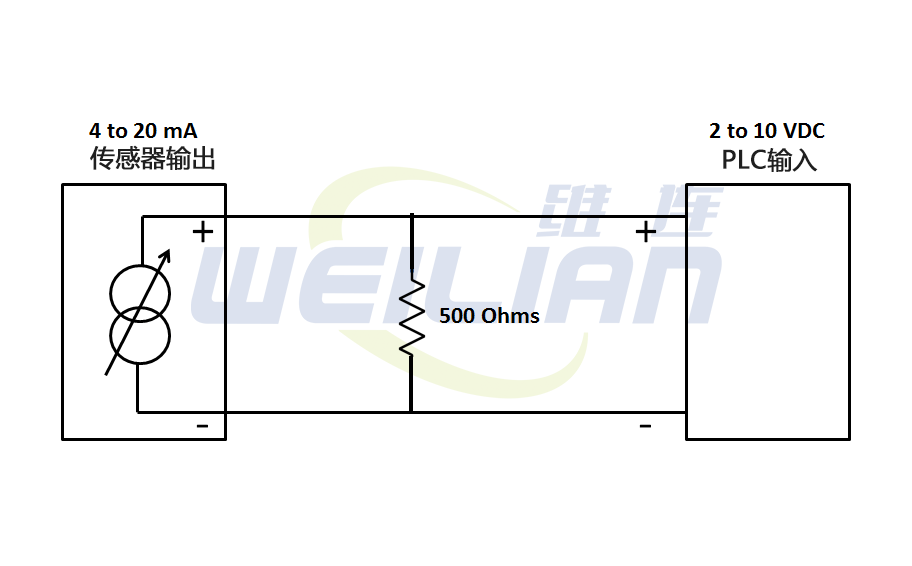
V = I*R = 0.004*500 = 2V
V = I*R = 0.020*500 = 10V
Example: The conversion of 0-20 mA to 0-5 VDC
Ohm's Law pointed out: R = V/i is voltage, i is current, R is resistance
R = 5V /0.020A = 250 ohm
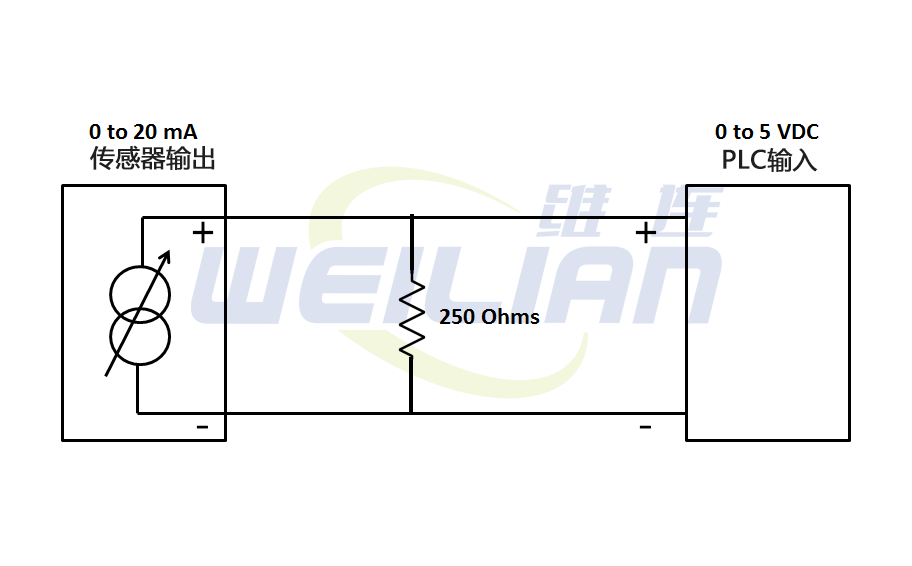
V = I*R = 0*250 = 0V
VIN = I*R = 0.020*250 = 5V
Note: -
● To avoid damage, you must ensure that external current sources have short circuit protection under all conductors.
● The external resistor is a source of error because it depends on temperature and its inaccurate.
● In order to obtain as accurate measurement results as possible, it is recommended to use the resistor as small as possible.

