
Resistance temperature coefficient
Resistance with temperature changes
Resistance temperature coefficient (TCR) is one of the most important parameters of the performance of the resistance of the resistor. TCR defines changes in the resistance as a function of the ambient temperature. The common method of TCR is PPM/° C (or PPM/° K), which means one -million -dollar of one million per degree Celsius (or Kelvin). resistance temperature coefficient Calculation is as follows:

Among them, the unit of TCR is PPM/° C or PPM/° K, R 1 is Ohm at room temperature, R 2 is resistance at work temperature, the unit is Ohm, T 1 is room temperature, T 2 is the working temperature ( Both are °) C or ° K). Usually, α is used instead of TCR.
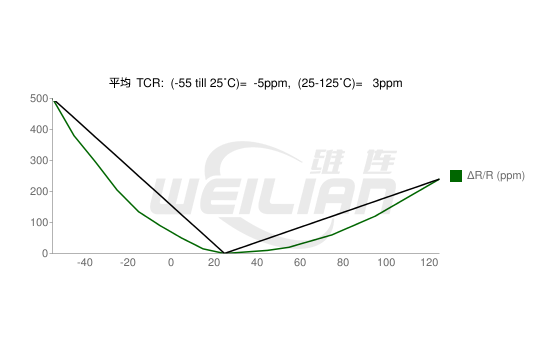
The average TCR ΔR/R (in PPM -unit)
The positive temperature coefficient of the resistance or negative temperature coefficient?
The TCR of the resistor is negative, positive or stable within a specific temperature range. Choosing the correct resistor can avoid the needs of temperature compensation. In some applications, larger TCR, such as measuring temperature. The resistors used for these applications are called thermistor , which can have a positive temperature coefficient (PTC) or negative temperature coefficient (NTC).
TCR measurement method
The resistance temperature coefficient of the resistor is determined by measuring the resistance within an appropriate temperature range. The TCR calculation is the average slope of the resistance in the interval. This is accurate for linear relationships, because TCR is constant at every temperature. However, many materials have nonlinear coefficients. For example, commonly used resistance alloy nickel chromium alloys have non -linear relationships between temperature and TCR. Because the TCR calculation is an average slope, it is very important to specify TCR and temperature interval. The method of measuring TCR is standardized in the MIL-SD-202 method 304. Using this method, you can calculate TCR from -55 ° C to 25 ° C and between 25 ° C and 125 ° C. Because the highest measurement value is defined as TCR,
The following table lists the resistance temperature coefficients of various materials. Please note that the accuracy depends on the purity and temperature of the material.
|
Material |
TCR /°C |
|
Silicon |
-0.075 |
|
/ |
-0.048 |
|
Carbon (non -fixed -shaped) |
-0.0005 |
|
Manganese copper |
0.000002 |
|
Constanttan |
0.000008 |
|
Nickel chromium alloy |
0.0004 |
|
mercury |
0.0009 |
|
Gold |
0.0034 |
|
Zinc |
0.0037 |
|
Copper |
0.0039 |
|
Aluminum |
0.0039 |
|
Lead |
0.0039 |
|
Platinum |
0.00392 |
|
Calcium |
0.0041 |
|
tungsten |
0.0045 |
|
tin |
0.0045 |
|
Iron |
0.005 |
|
Nickel |
0.006 |
|
Lithium |
0.006 |
The value of TCR depends on purity and temperature.

