

Understand NTC thermistor temperature sensor features
The electrical characteristics of the NTC thermistor are combined to describe the resistance and temperature response of the thermistor sensor. Understanding this is very important for choosing a more suitable thermistor sensor for given applications. The specifications of all PAN series have the following characteristics:
Named resistance@25 ° C (ω)
● Provide a reference required to calculate the resistance at any other temperature within the temperature range of the computing sensor.
● Allows to select the correct sensor as a point matching or curve matching application.
resistance temperature coefficient α, α (%/° C)
● Zero -power resistance phase of temperature change.
● Indicates the slope or sensitivity of the resistance and temperature response of the thermistor and the temperature response.
Digital difference (5%, 3%, 2%, 1%)
● By multiplied by resistance temperature coefficients , the given temperature is obtained.
Temperature tolerance (1.0 ° C, 0.5 ° C, 0.2 ° C, 0.1 ° C)
● Indicates the deviation of the RT curve (based on the degree of degree Celsius).
● Within a specific curve matching temperature range, the temperature difference is the same.
● Generally, the resistance of the resistance is specified with the heat -sensitive resistance.
Hot time constant (second)
When the section jump function changes under zero power conditions, the duration of 63.2% of the difference between the initial temperature and the final body temperature changes between the thermistor.
Temperature accuracy (ºc)
● Calculate to the resistance to the resistance to the temperature coefficient (alpha). Given the same Alpha, better tolerance can produce better accuracy.
Maximum rated power (MW)
● Thermistor will be accepted while maintaining its characteristic stability, and it will dissipate a maximum power (in the units of millwathes) in a longer period of time.
Beta tolerance (1.0%)
● Suitable for all TR series NTC thermistor sensor
Disposal constant (MW/° C)
● At a specific environmental temperature, the ratio of power consumption and body temperature changes in thermal resistance is represented by millwatter/degree Celsius.
Material constant beta, β (° K)
● The shape of the RT curve is the amount of resistance at a temperature at a temperature at another temperature.
● Use Beta equation to calculate and expressed it with Kaishi (° K).
● Beta equation requires two RT datasets, which is accurate enough for most industrial requirements.
● Unless otherwise explained, Beta is calculated using a temperature range from 25 ° C to 85 ° C.
Calculate resistance temperature
Steinhart-Hart (° K) or Beta (ß) equations can be used to calculate. Steinhart-Hart is more involved in the two, but it is more accurate because three RT datasets are required instead of two.
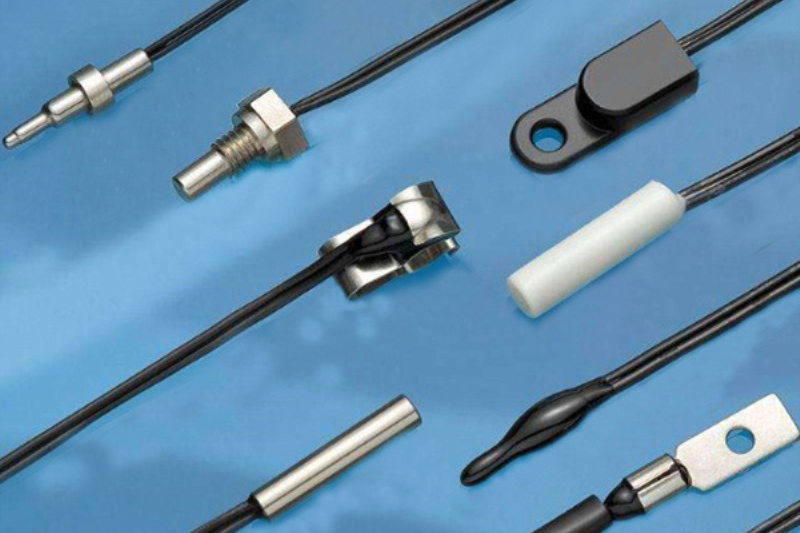
Heat resistance temperature sensor series selection table
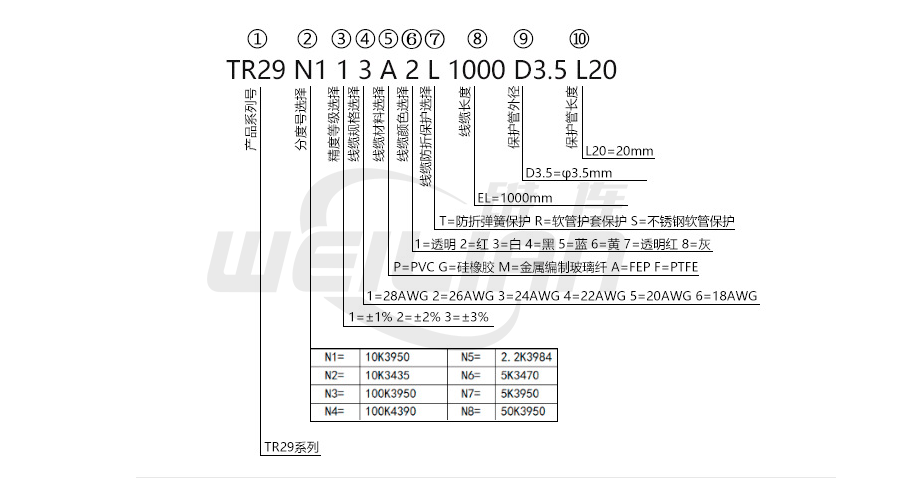
TR thermistor resistance temperature sensor series list
(probe component / epoxy resin)
Epoxy resin immersion NTC thermistor welding between the TeFLON / PVC wire with a cover < / p>
(probe component /circular terminal)
Epoxy resin immersed NTC thermal resistance packaging In the tin -plated copper ring -shaped wiring sheet
(probe component /threaded metal tube and hexagon)
NTC thermistor is packaged at the tip of the durable stainless steel alloy tube, with a tapered thread hexagon screw
(probe component /closed metal tube)
NTC thermal resistance internal durable stainless steel alloy tube and epoxy resin filling
Probe component /thread tip and hexagonal)
NTC thermistor is covered in an aluminum hexagonal screw, straight thread
When you find a sample that is most suitable for your project, we always provide free samples. If you are not sure, please contact our engineer, they can help you determine which TR thermistor temperature sensor is suitable for you.

